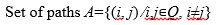All published articles of this journal are available on ScienceDirect.
An Effective Mathematical Programming Model for Production of Automatic Robot Path Planning
Abstract
Objective:
Path planning for production robots has been investigated. The sequence of the orders to be processed in a certain planning horizon has been planned for the production of system.
Methods:
Production of automatic robots are employed to carry parts and products among all production stations and machining centers. The combination of machines in stations and autonomous robot evolves a production network.
Results:
The problem is to assign orders to robots so that paths are obtained to minimize total waiting times of production system and meanwhile provide collision-free paths.
Conclusion:
The proposed mathematical formulation is implemented to show the efficiency and effectiveness.
1. INTRODUCTION
Traditionally, Autonomous Guided Vehicles (AGVs) were mostly used at manufacturing systems, but currently, other applications of AGVs are extensively developed in other areas, such as warehouses, container terminals and transportation systems. The problem of path planning for AGV is a significant case while multiple AGVs are employed in the system [1-3]. An, Automated Manufacturing System (AMS) is a complex network of machines and devices so that demands are fulfilled and production tasks are determined for all components accordingly [4].
For the methods and techniques of path planning, different aspects are studied in the past. Unlike previous stochastic optimization methods which use expected values instead of probability distribution as length or cost of each arc in stochastic methods [5] proposed a novel general stochastic dynamic programming approach which is not only a dynamic method but a static method which also generates integrated probability functions at the end of each path in networks and compares probability distributions instead of expected values of each arc to find the shortest path in the network. In addition [6], this method has been implemented on different combinations of probability distributions and the results are compared on the basis of cost criterion to show the superiority of his developed method [7, 8]. Olya [9] analyzed the computational efficiency of the developed algorithm using maximum likelihood estimation and moment generating function in a simulation environment.
The effect of delay on path planning is significant due to the impact of on-time delivery for customer satisfaction. Also, collision-free decision making is challenging and leads to incur delay on the production schedule. Thus, the trade-off between delay and collision needs to be considered for optimal path planning.
In this paper, a general path planning mathematical model for autonomous production of robot system has been proposed in a network. The aim of the model is to minimize the delay and thus the costs of transportation. The remainder of our work follows here. Next, the related literature is reviewed. In Section 3, the problem is justified and described. In Section 4, the proposed mathematical programming approach has been discussed. Numerical experiments are presented in Section 5. Conclusion is presented in Section 6.
2. LITERATURE REVIEW
In the literature, researchers investigated the design of an AMS and planning for the components being employed.
Fazlollahtabar and Saidi-Mehrabad [10] categorized the related literature for different scheduling and routing methods of autonomous robots in different problems such as distribution, transshipment and transportation systems.
Fazlollahtabar et al. [11] analyzed material flow optimization for a flexible job shop automated manufacturing system. The aim was to balance the material flow carried by robots through the production stations. M’Hallah [12] investigated job scheduling having different processing times and similar due dates on a single machine for total tardiness and earliness minimization. Ueno et al. [13] considered the concept of virtual obstacles in path planning problem and developed a robust algorithm for optimization. Gerstl and Mosheiov [14] considered scheduling problem for competing agents being processed on the same machine and developed a solution algorithm. Igari et al. [15] developed a computer-aided operation planning for machines and tools based on database data retrieval concept. Mi’radj Isnaini and Shirase [16] studied general process planning using computer-aided mechanism. Hamidinia et al [17] considered a novel complex single-machine scheduling problem and proposed two solution methods. Fazlollahtabar and Mahdavi-Amiri [18] proposed a bi-criteria optimal path planning in a flexible job shop manufacturing system. Their model was associated with a comprehensive analytical study on the optimality of the hierarchical decision made by the optimal path method. Fazlollahtabar and Mahdavi-Amiri [19] designed a cost estimation expert system using a fuzzy rule backpropagation network that provided the cost estimation in an uncertain autonomous production network. Fazlollahtabar and Olya [20] proposed a heuristic statistical method to compute the total stochastic material handling times by autonomous robots and to find an optimal path for an advanced production system.
Yokozuka and Matsumoto [21] investigated energy minimization path planning problem where robot energy consumption was significant for tactical decision-making level. Fazlollahtabar et al. [22] considered due dates of multiple autonomous robots as a criterion to analyze delay composing of earliness and tardiness; then an integrated heuristic algorithm was developed as a solution method.
Fazlollahtabar et al. [23] introduced a new concept of a turning point and developed a complicated problem of concurrent routing and scheduling for multiple autonomous production robots. The aim was to provide conflict-free and deadlock resolution.
Ishikawa et al. [24] analyzed the problem of path planning with respect to the geometry of the agents. For further studies on path planning problems and methods, the readers refer to Fazlollahtabar and Saidi-Mehrabad [25].
3. STATEMENT OF THE PROBLEM
A production system that contains several machining centers is considered. In any machining center, different types of machines exist to process the required tasks according to the process plan. Robots are used to carry parts to be machined at the machining centers and in their corresponding machines. A network of machines and paths is configured so that robots move on the paths. The sequence of independent operations is pre-specified. The machines positioned in the same machining center have similar properties, such as the same need of operator proficiency, similar functionality, and toolbox resemblance. The objective is to find a path plan for each production of autonomous robot, minimizing total waiting time, while the costly collision of robots is avoided. The assignment of orders to robots is handled using a mathematical model. An overview of the problem is depicted in Fig. (1).
While several robots function in the proposed production, network challenges of robot collision are inevitable. The repair and downtime incur extra costs to the system and lead to backlogs of orders and lost sales. Another issue is the violation of cycle time which directly influences the demand satisfaction. Therefore, developing a mathematical model to handle collisions in robot path planning could be significant.
To formulate the proposed path plan, the due date for delivering a part to a machining center is considered to be the earliest processing time and the upper bound is the cycle time of the production system. Any time out of that window is assigned a penalty cost. In other words, if the robot delivers earlier than the lower bound then an earliness penalty is assigned, and if it arrives later than the upper bound then a lateness penalty cost is incurred.
In the beginning, robots are parked at the parking lot. Then, machining centers call robots for handling the parts at the machining centers according to the process plan. The robots may occupy the same paths and collide. Then the path plan should be triggered to prevent the collision of robots. On the other hand, the robots should be allocated to the paths so that waiting times are minimized. Thus, a mathematical model is proposed to both prevent collision and minimize the total waiting times of robots.
4. PROPOSED MATHEMATICAL FORMULATIONS
In this problem, a robot should arrive at a machining center within its due date window to handle the transfer action otherwise:
- If it arrives early, a waiting time is incurred;
- If it arrives late, a buffer (and bottleneck) is formed leading to be behind the process plan and causes the delay in demand fulfillment to be penalized as lateness cost.
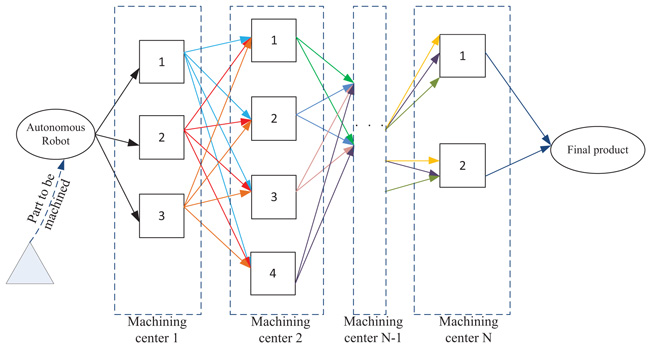
The mathematical notations are listed below.
4.2. Parameters:
| dij | Distance between two machining centers or nodes i and j (in meter scale) |
| av | Average velocity of vth robot (meter/second) |
| gv | Unit movement cost of vth robot ($) |
| tiv | Arrival time of vth robot to ith machining center (second) |
| Pl | Penalty for one unit of delay ($) |
4.3. Decision Variable:
Assignment of vth robot to a path connecting ith and jth machining centers
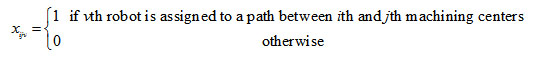
A slack variable
4.4. Objective Function:
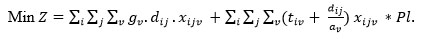 |
(1) |
which is minimizing the transportation cost and delay penalties. The first term of the objective function is to compute the vth robot movement cost between ith and jth machining centers. The second term is minimizing the delay penalties of robots arrival to machining centers.
4.5. Constraints:
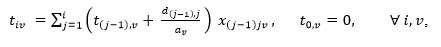 |
(2) |
The constraint is related to interval time for robot which is to determine the robot arrival time to a machining center.
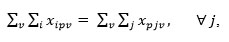 |
(3) |
The constraint certifies that each entering robot to a machining center will certainly exit (note that p is a counter for machining centers).
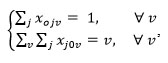 |
(4) |
The constraint expresses that robots are located at central machining center sent to a machining center to process handling task and after that return to the original position. By 0 the model shows the robots parking machining center.
 |
(5) |
The constraint certifies for each movement between any two machining centers, only one robot is assigned.
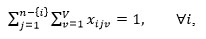 |
(6) |
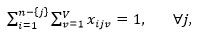 |
(7) |
The two constraints certify that only one arc is entered and exited from a machining center (n is the number of machining centers).
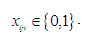 |
(8) |
The relation shows the type of decision variable.
5. NUMERICAL STUDY
Here, to implement the proposed mathematical model of path planning, a numerical example is presented. Here, a medium sized problem with the following specifications is designed:
Number of machining centers: 8,
Number of robots: 3,
Average velocity of robots: 3m/s,
Unit costs of traveling are 5, 9, 11, for all robots, respectively,
The distances among all machining centers are a 8*8 matrix:
d= 0, 2, 4, 5, 7, 8, 10, 14,
2, 0, 1, 2, 6, 7, 9, 13,
4, 1, 0, 3, 4, 5, 10, 12,
5, 2, 3, 0, 2, 6, 11, 14,
7, 6, 4, 2, 0, 1, 4, 7,
8, 7, 5, 6, 1, 0, 3, 5,
10, 9, 10, 11, 4, 3, 0, 4,
14, 13, 12, 14, 7, 5, 4, 0;
Robots should arrive at a machining center in the due time to handle the material to the next machining center. If it arrives early or late then a waiting time is incurred and penalized by a cost of Pl=7.
Using the above data, we optimized the mathematical model in GAMS software. The obtained decision variables resulted from GAMS optimization software, are shown below in Table 1.
The objective function value obtained from the mathematical model is 72. The assignment of robots to machining centers and the path plan is shown in Fig. (2).
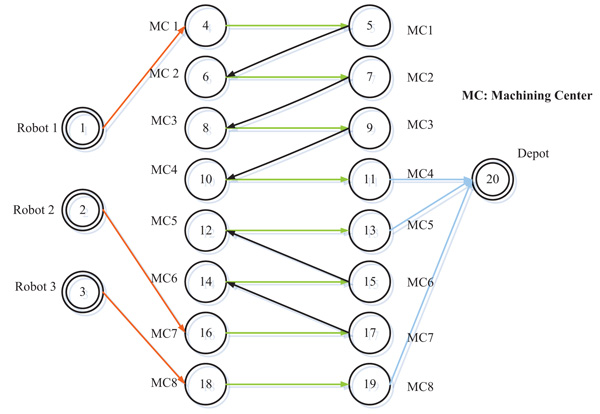
Fig. (2) shows that the first robot is assigned to machining center 1 and then takes the parts to center 2, 3 and 4, respectively and then moves to the depot. Then, robot 2 is allocated to machining center 7 and moves to 6, 5 and finally to the depot. Robot 3 is also called from machining center 8 and takes the final product to the depot.
A comparative analysis is performed to verify the efficiency of the proposed model. It has beenet al. considered to increase the delay penalty cost and run the model again to investigate the effects. Here, the penalty is increased to 12 unit of const. Then, the objective function value is 68; the reason is that the model obliges the robots and machines not to have a delay as much as possible.
In the second experiment, we decrease the distances between any two machining centers and evaluate the outputs of the model. The results show that the objective function value is increased to 85 and the reason is the impact of collision regarding shorted distances leading to more delays.
Therefore, the model is valid for different circumstances.
CONCLUSION
This paper formulated the robot path planning problem in a production system having multiple robots and machining centers in a network configuration. The waiting time, lateness, and collision were considered in the model. The objective was to provide paths having a minimal delay and moving costs for different robots. The main contributions of the problem include collision challenge in the modeling, and considering delay concept for robots. An illustrative example worked out to imply the applicability of the mathematical model. The results showed that the optimal assignments of robots to paths provide minimal distance moved by robots and minimal delay composing of delays. For future research, the following suggestions are recommended:
- Considering capacitated robots in modeling
- Including uncertain movement time and cycle time
- Developing the periodic dynamic formulations for multi-period production system
- Considering robot failure and maintenance costs in the modeling
CONSENT FOR PUBLICATION
Not applicable.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The author declares no conflict of interest, financial or otherwise.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
Declared none.